Radiology or so-called medical diagnostic procedures is a series of different examinations on different parts of the body, using methodologies based on ionizing radiation, electromagnetic fields or ultrasound waves, which through software processing give a picture of the morphological anatomical state of the human body.
Radiology is a branch that is advancing on a daily basis with advances in technology and in the field of diagnostics, but today in treatment. It has played a major role in the oncology field and intervention procedures.
Diagnostic radiology incorporates digital technology that delivers precise and clear picture of changes, minimizing risk across the patient.
There are three types of radiology, namely, diagnostic radiology that uses X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds and nuclear medicine, which allows images to be analyzed to diagnose a disease or health problem. Oncological Radiology, the use of radiation to treat diseases such as cancer and interventional radiology, which uses imaging tools to diagnose and treat diseases and disorders using X-rays, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging, enabling clinicians to procedures with minimal invasive treatments.
There are the following diagnostic procedures
Methods carried out by ionizing radiation
Digital X-ray
Digital Mammography
Osteodensitometry
Multislice Computed Tomography
Methods carried out by ionizing radiation and open sources of radioactive radiation, radioisotope
Positron emission computed tomography
Methods that do not use ionizing radiation
Magnetic resonance imaging
Ultrasound diagnostics
If you have any questions, please contact us at: [email protected] or +389 (0) 44 344 414
To schedule an examination, click here
Categories
A method used to determine bone density by a DEXA scan indicated by an orthopedic surgeon, physiotherapist or endocrinologist. The apparatus operates with x-rays which are of very low permeability for this technique.
When imaging a patient, the presence of a person who does not have a personal dosimeter is strictly forbidden.
The recording takes a short time of about 10 minutes and results are immediately available. Patients for this imaging are not subject to any prior training and are scheduled during working hours. Because of the use of x-rays, women in their reproductive period must be asked if they are pregnant because pregnant women are either not imaged or are extremely rare with radiologist approval.
After receiving the result, the patient is consulted with the referring doctor.
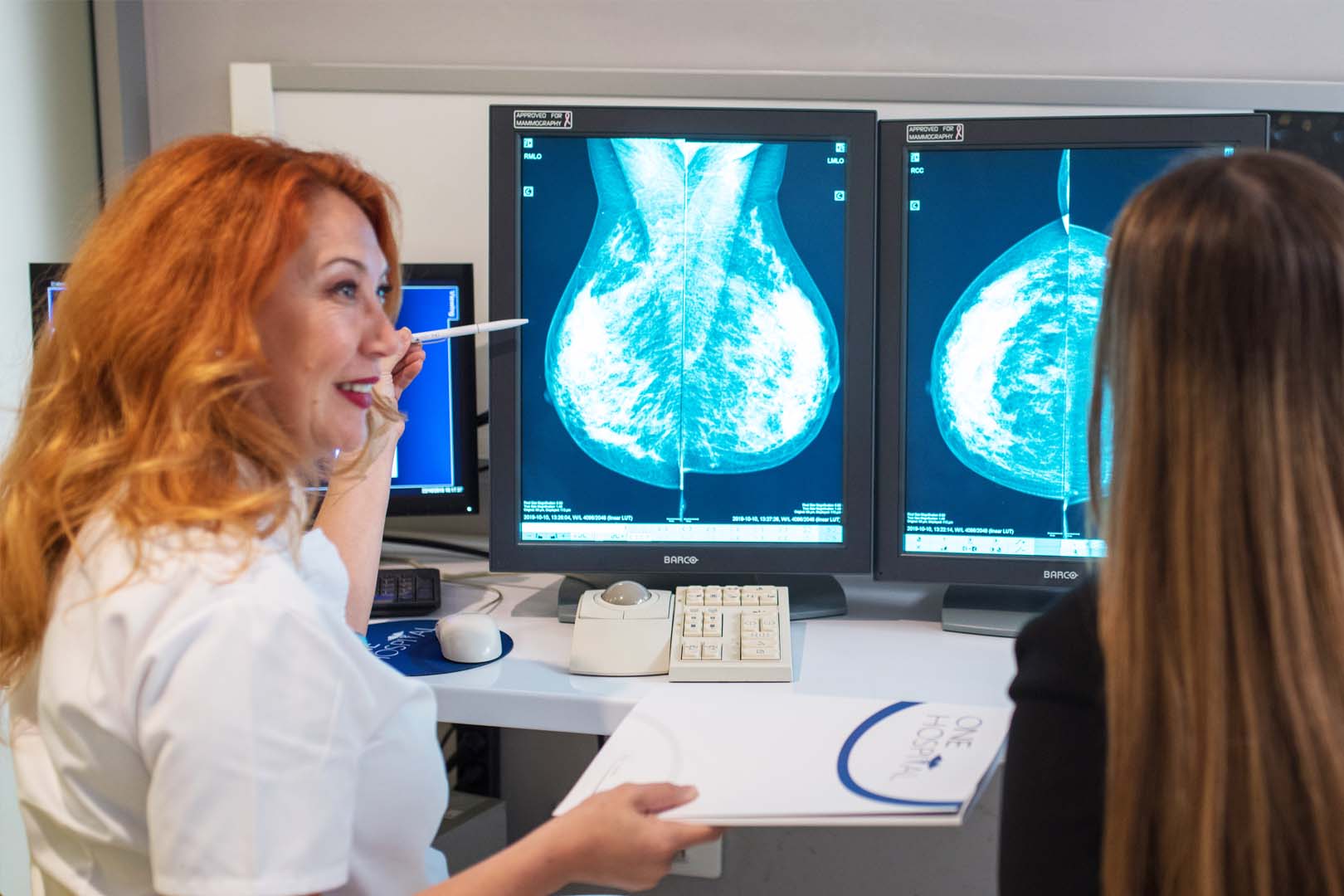
Mammography is a method that uses a special type of so-called “soft” ionizing radiation that, with its penetration, provides accurate data on the condition of the parenchyma in the breast or the change previously detected on ultrasound examination.
For this imaging, it is very important for patients to be scheduled between 5-10 days of menstrual cycle as the glandular tissue is then without an edematous hormone response. This method is mandatory for women over 40 years of age compulsory as part of a breast screening examination every second year. Upon doctor’s suggestion it can be done earlier.
Because of the use of x-rays, women in their reproductive period have to inquire whether they are pregnant because pregnant women are either not recorded or are extremely rare with radiologist approval.
How is it performed?
Dress comfortably. When shooting an X-ray technologist places the breast on a detector and gently presses it with a plastic plate. The pressure may be slightly unpleasant, but no pain should be experienced. Recordings are made in two positions on each breast and after completion of the examination the patient is free for daily activities.
The recording process takes up to 30 minutes.
In our hospital X-ray machine is one of the most modern devices because it uses digital processing of X-ray graphics. It has two large digital detectors that allow for very low-level image acquisition, as well as a significant reduction in the number of failed images and patient mirroring.
This method is the first choice for bone joint injuries, suspected bone fractures, joint dislocation as well as deformities and swelling. It is also used as a diagnostic method for rapid lung diagnosis, especially for suspected pneumothorax, as well as for acute exudate, inflammation, acute and chronic lung obstruction. It is also used to record the gastrointestinal and urogenital system, especially as it is the first method of choice for suspicion of ileus, and is also used for suspicion of calculi in the urinary tract.
The method is noninvasive using a small dose of radiation but it is very important to note that the patient should not be recorded on his own request without a prior examination and referral from a doctor. Pregnant women are either not recorded or recorded extremely rarely with radiologist approval.
Breast ultrasound is a safe, non-invasive diagnostic procedure that delivers images of the interior of the body using sound waves. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel to the body. No ionizing radiation is used during ultrasound examinations, in particular no radiation exposure to the patient. Used for regular checkups and diagnostics of breast lumps or other abnormalities your doctor may have discovered during a physical examination. It is best to see a doctor if you are experiencing a change yourself.
When should you be examined?
The examination is safe and can be done at the youngest age and in adolescents.
For women of childbearing age, it is optimal to be between the fifth and tenth days of your cycle. This procedure requires a little preparation of the body.
How is the examination performed?
The patient is admitted by a nurse who will place in a position of examination. The patient is lying on her back with her arms raised over her head. You may also be prompted to change positions during the review. Apply a water-based probe gel. The probe is applied to the body and moves back and forth through the area of interest. Wear comfortable, comfortable clothes. Ultrasound gel does not dye or discolor clothing. Breast ultrasound is usually performed in 30 minutes. After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to return to your normal activities immediately.
A non-invasive simple thyroid detection, evaluation method for thyroid changes. The patient is lying on a table with his/her head raised and a gelatinous pillow is placed under his/her neck to completely extrude the region of the examination.
A linear probe gel is applied and scans are performed using ultraviolet waves that give information on the morphology and structure of the thyroid gland, as well as its blood flow. When detecting a change, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist or pathophysiologist. If it is changed for a biopsy, it is accessed.
The diagnostic procedures may show certain changes in the form of cheekbones, deep changes in soft tissues, breasts or glands.
During the detection of such changes in soft tissues, breasts, thyroid or fluid-containing muscles a small-needle biopsy and fluid evacuation is being performed.
How is the procedure performed?
The procedure itself is ultrasound controlled to ensure that the material is taken from the right place.
The method is low-risk and simple, and provides an appropriate cytological diagnosis.
No prior preparation of the patient is required.
Be sure to tell your doctor about your monthly cycle or if you have been taking anticoagulant therapy.
Procedure
An ultrasound scan is performed prior to the procedure for accurate localization of the site of interest. It is then sterilized to reduce the risk of infection infections.
The ultrasound places the needle which is thin and feels first a little pressure and pain that is similar in intensity to the pain of taking blood. The extracted content is analyzed cytologically.
The data obtained from the analysis provide insight into whether it is of benign or malignant origin.
When is the procedure performed?
The procedure is always performed after a doctor’s indication of various cystic changes of the breast, thyroid gland, fluid collections in the soft tissue, etc.
A method of taking a small needle mold that is of varying thickness from a change that is detected by different diagnostic methods.
The procedure itself is ultrasound-guided to ensure accuracy of material sampling and appropriate histopathological diagnosis.
CORE biopsy can be performed on changes in the breasts, muscles or available bone parts where different thickness needles are used depending on the change.
Of course, in order not to be too painful and unpleasant for the patient, a local anesthetic is applied.
Computed tomography is a non-invasive diagnostic method that uses ionizing radiation with certain permeability and by software processing the data obtained during the scan itself provides accurate localization of the type and change to be detected within the body. This is a non-invasive method that examines the bones, soft tissues, thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity and blood vessels. Quick and simple, it is the first choice in polytrum and emergency vascular incidents.
How does a Computed tomography works?
An X-ray tube that rotates in a so-called “gantry” releases a beam of ionizing radiation that passes through the patient’s throat and is intercepted by detectors housed in the very mass on which the patient is placed. Data in different shades of black to gray that are actually specific to each organ.
Processing data is displayed in both 3D and color.
How is it performed and what should the patient know?
The patient should be informed that he / she should be hungry for at least 4 hours, prior to the examination itself. The X-ray technician prepares the patient by suggesting that in some examinations a liquid contrast or water may be needed to fill the intestines.
Before the examination itself if intravenous contrast is needed, results of urea and creatinine in the blood should be submitted to determine the status of the kidneys. Then the patient lies down on a computer tomography table moving around in a circle called a “gantry”. The recording itself takes from a few minutes to half an hour depending on what the scan is exactly and whether intravenous contrast is applied.
The patient needs to be calm and when the X-ray technologist tells him/her to stop breathing because inappropriate examination behavior leads to artifacts. After the recording the patient is free to go home.
What exactly does a Computed tomography detects?
Musculoskeletal system problems
The brain
Fractures
Tumors
Cardiovascular system condition
Detection of lung conditions
Pathological changes of all organs in the abdomen
Method for conducting biopsies
Why contrast computed tomography?
The computed tomography shows great bone density, but soft tissues are insufficiently presented as well as blood vessels.
An intravenous contrast, which is an iodine preparation, is given to show clearly.
Since it is excreted by the kidneys, it is recommended to drink a larger amount of water after the imaging is taken.
What does the doctor need to know before imaging?
You must tell your doctor whether you are pregnant, the therapy you are taking daily and for a long time, especially if you are taking metformin. Our hospital is equipped with a hybrid 16-layer PET CT scan.
PET/CT is an imaging technique consisting of a combination of: PET (positron emission tomography) that shows the functions of organs and tissues at the metabolic level, and CT (computerized tomography) that provides detailed anatomical information.
What can be revealed with PET/CT?
This technique can detect even the smallest metastatic changes, commonly used to diagnose early cancers, heart problems, brain problems and disorders including brain tumors and memory problems, as well as other neurological disorders.
Is PET/CT recording harmful?
PET/CT is performed using a radiopharmaceutical, and the most common radioisotope used is FDG-18F. is minimal and this recording is completely safe. It is used in both children and adults, and the doses used are minimal and do not affect the normal processes of the body.
Can the patient eat before PET/CT scan?
No. Before being started with PET/CT imaging, patients receive guidance on imaging preparation, which includes a specific diet regimen in order to obtain accurate results. On the day of the shooting, patients should not eat chewing gum (since they contain sugars, and elevated blood glucose levels can produce quite different results). You can only drink water.
How is the recording performed?
Before the recording begins, the radiopharmaceutical is administered intravenously and for the best accumulation in the body, should be for 45 minutes. During shooting, you are in a lying flat bed positioned in the center of the cylinder scanner. The recording takes 30 minutes.
Can you continue your activities after the recording?
Yes, absolutely. Immediately after recording you are able to resume your normal activities. We recommend consuming a lot of liquids to eliminate contrast and radiopharmaceuticals.
How long do you get results?
Our specialist radiologists, after recording the findings, prepare a report and report and submit the results. You get the results in a day, including a second opinion from top Turkish radiologists.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a method that uses electromagnetic field and radiofrequency energy to activate the hydrogen ion in the human body which, with software processing, provides accurate information and precise detail at the tissue level.
It should be noted that this method is completely safe, non-invasive, does not use X-rays or any other type of radiation, so access is permitted to all medical personnel except persons who have implanted a metal implant or pacemaker. Because it does not use radiation, small children and pregnant women can be shot.
Imaging lasts from 20 minutes to 45 minutes, so patients in serious condition should first stabilize and then imaging on this device or performs the imaging under the supervision of a physician who will be present at the imaging.
Because it uses a strong magnetic field, patients with non-titanium metal implants in the body and patients with pacemaker are not shot. Also, the room must not include a clock, cell phone, credit cards, coded keys and anything that works on batteries because the magnetic field will magnetize and stop functioning.
This method is most commonly used for brain imaging, spinal cord, joints, glands, and less often for lungs and abdomen with a small pelvis. Angiographic scans of blood vessels can also be done. Some imagings are done in contrast and some are only in the native series, but among the imaging that are most often and almost compulsorily applied are:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen, pelvis, pituitary gland, orbits as well as angiographic imaging.
Patient preparation depends on whether the imaging is in contrast or in native series. If contrast is not applied preparation is not required. The patient lies on a moving table, and depending on the segment of interest, coil or so-called antennas are received that receive a signal emitted by the body in a magnetic field and assist in image processing software. During some examinations, headphones are set up with different music as the instrument produces sounds.
When contrast is taken, the patient should go hungry three hours prior to the examination and since the contrast medium is eliminated by the kidneys he/she should be brought to a laboratory with urea and creatinine results in the blood to monitor renal function.





